UX and UI: Understanding the Roles in Web Design
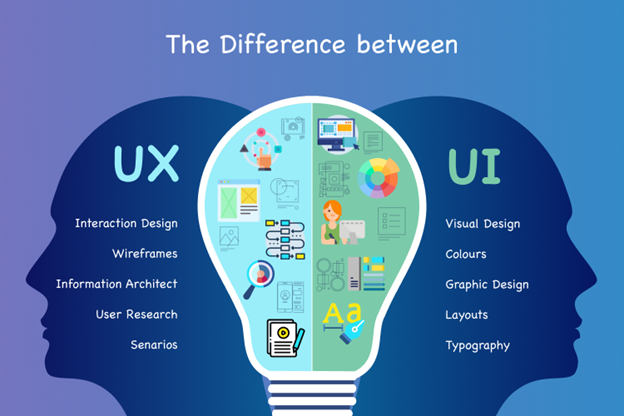
Therefore, UX focuses on the user’s experience, and UI focuses on the visual interface elements such as font, colours, menu bars, and more.
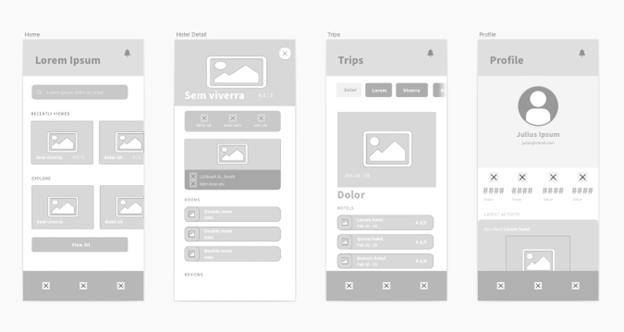
The foundation (UX) should be established first, including how each webpage links to the others and where the links should be placed for functionality and practicality.
Once the framework is in place, the next step would be about interior design elements, such as how to hang images appealingly, choose elements that complement the website’s colour, and arrange different sections so that they are easily accessible without making the space appear too cluttered.
This illustrates how UX and UI designers’ roles are divided when working on a website. The logical flow of activities and core components is established first, followed by the definition of visual details. It also shows how the collaboration works, with UX designers handing over their recommendations and work to the UI team after the fundamental ideas have been tried and tested.
Evolving Landscape of UI/UX Roles
The roles of UI and UX are constantly changing. Web designers are individuals who create online software or goods. The more explicit concepts of UX and UI and their differences have recently become widely discussed as the design business has grown.
However, due to the app and product design industry’s continued rapid expansion, more specialised positions and titles, such as UX Writer, content designer, and interaction design, are constantly emerging.
Our conception of design is continuously changing. That is a big part of what makes it such a fascinating field. So, while having an analogy that illustrates the position on the UI/UX issue is helpful, always keep an open mind and decide what is best for the user.
What is UI design?
Typography, pictures, and other visual design components are used in user interface (UI) design to make a simple interface understandable and usable. The process of turning wireframes into a finished graphical user interface is known as UI design.
This improves a product’s usefulness while also forging an emotional bond between the user and the product. Therefore, a user experience (UX) is made up of numerous user interfaces (UI), which combine to create a product in an (ideally) seamless flow.
As its focus is evident from its name—interfaces—we may define the boundaries of UI in a much more concrete way than UX’s. The total impact of a series of interfaces and all the additional, less obvious aspects of a product’s experience make up the user experience. In contrast, UI is solely focused on the impact each screen or interface’s design will have on the user’s journey.
What does a UI designer do?
A UI designer’s task starts at the prototyping stage, whereas a UX designer’s job stops. They take the wireframes and incorporate visual design to improve usability, aesthetics, and screen size compatibility.
A UI designer focuses on how a design’s colours, typography, and graphics relate to a product’s brand. Let’s examine the typical responsibilities of a UI designer in more detail below.
The look and feel of a product
- Design research: Research reveals information on users, rivals, and the newest trends in design. Find inspiration and produce user-friendly interfaces.
- Visual design: UI designers are in charge of creating the user interface’s visual components, such as colours, fonts, icons, buttons, and more.
- Graphic design and branding: The product’s brand positioning significantly impacts the user interface (UI) design. The correct balance between usability and continuously displaying the brand identity specified by the marketing or creative team must be struck by designers. As a result, graphic design and UI design are tightly intertwined.
- Design systems: UI designers develop style manuals, pattern libraries, and components that specify how each element should appear to assure uniformity between products and brands.
Responsiveness and interactivity
- Animation and interaction: UI designers can create an interface’s interactivity via animations, transitions, or other interactive features.
- UI prototyping: A live demonstration of every UI component and design interaction. UI designers produce them for user testing and understanding how the product will operate.
- Responsive design: Interfaces must effortlessly adapt to all platforms, devices, and screen sizes in terms of form and function.
What is UX design?
Understanding the users’ complete journey and translating it into a product are the goals of UX design. The entire user experience, from beginning to end, is referred to as UX design. It tries to solve the question: How can I make it as easy and frictionless as possible for individuals to attain their goals?
In other words, UX design is focused on a customer journey’s total user-friendliness. Additionally, there is substantial disagreement over the beginning and end of UX because of different opinions and whether ideas can be functional. This can be prevented from being more straightforward or perplexing, depending on the stage of the design framework. So, let’s explore what UX design implies below.
What does a UX designer do?
A user experience designer’s responsibility is to comprehend the consumer journey. This includes developing user flows, creating user testing procedures, interviewing customers, and understanding the target audience. Let’s examine the typical responsibilities of a UX designer.
Research and strategy
A UX designer develops a strategic plan at the start of the UX design process to ensure all stakeholders are on the same page and pursuing the same objectives.
While people frequently associate design with the visual, a UX designer’s work consists primarily of conceptual problem-solving based on research and data.
Information architecture (IA) focuses on classifying and organising the material of a website, mobile application, or other product. The objective is to assist users in finding information and achieving their goals.
Wireframing and Prototyping
The UX design process begins with user interviews to identify their needs, followed by creating the optimum user flows to facilitate task completion. Because of this conceptual emphasis on the user journey, a UX designer has little control over the actual and final appearance.
The most effective way for a UX designer to determine whether they’re performing their job correctly is through testing. Testing on actual customers. UX designers can gather user information to confirm their ideas and hypotheses by testing early in the design process with a rough prototype or a paper mockup.
- Wireframing: A wireframe is essentially the skeleton of an interface, providing the most basic understanding of how a design will function. It can either be hand-drawn on paper or created digitally.
- Analysis: UX designers collaborate closely with product managers and researchers to interpret test results and determine the following steps.
Why is UI and UX important?
The mixture of UX and UI shapes the whole online experience with a product. Even while two similar products might yield the same result, their UX/UI will differ in how they deliver it.
Users will use a product or service more frequently if it has a better UX/UI design than competitors. Great UX is no longer merely desirable; it is now expected. 70% of customers with poor UX will switch to the rival. Some goods are successful because they deliver excellent experiences.
How do UX and UI work together?
UX and UI are not wholly independent things despite their differences. On the contrary, each factor influences the other. Both are important and intimately related to how a website looks and performs.
Imagine spending hours designing a beautiful website only to discover that users struggle to navigate it. Users will become dissatisfied and leave the site regardless of how appealing the interface is if the UX needs to be improved.
On the other hand, consider a scenario where user testing and research are done to offer users the best possible user experience. For example, If a website’s text is too light, visitors can easily read it. If the UI is unpleasant, users may be discouraged from discovering more about the product or service, even if the UX is excellent.
To put it simply, UI exists without UX and vice versa. Therefore, to ensure that users can interact with the product or service efficiently and enjoyably, businesses will require both elements while designing a user-centric product.
Conclusion
User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) play essential but distinct roles in the design. UX focuses on creating a seamless and user-friendly journey for individuals, emphasising problem-solving and understanding user needs.
On the other hand, UI centres on the visual elements of the product, including typography, colours, and layouts, to make it aesthetically appealing and understandable.
ARCC specialises in website design services in Singapore, strongly emphasising UI/UX front-end design. Our designers and developers are dedicated to creating visually stunning and user-friendly websites that leave a lasting impression. Reach out to us today to learn more.